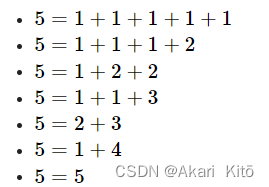DP专题
跟着ygg的dp题单刷的dp
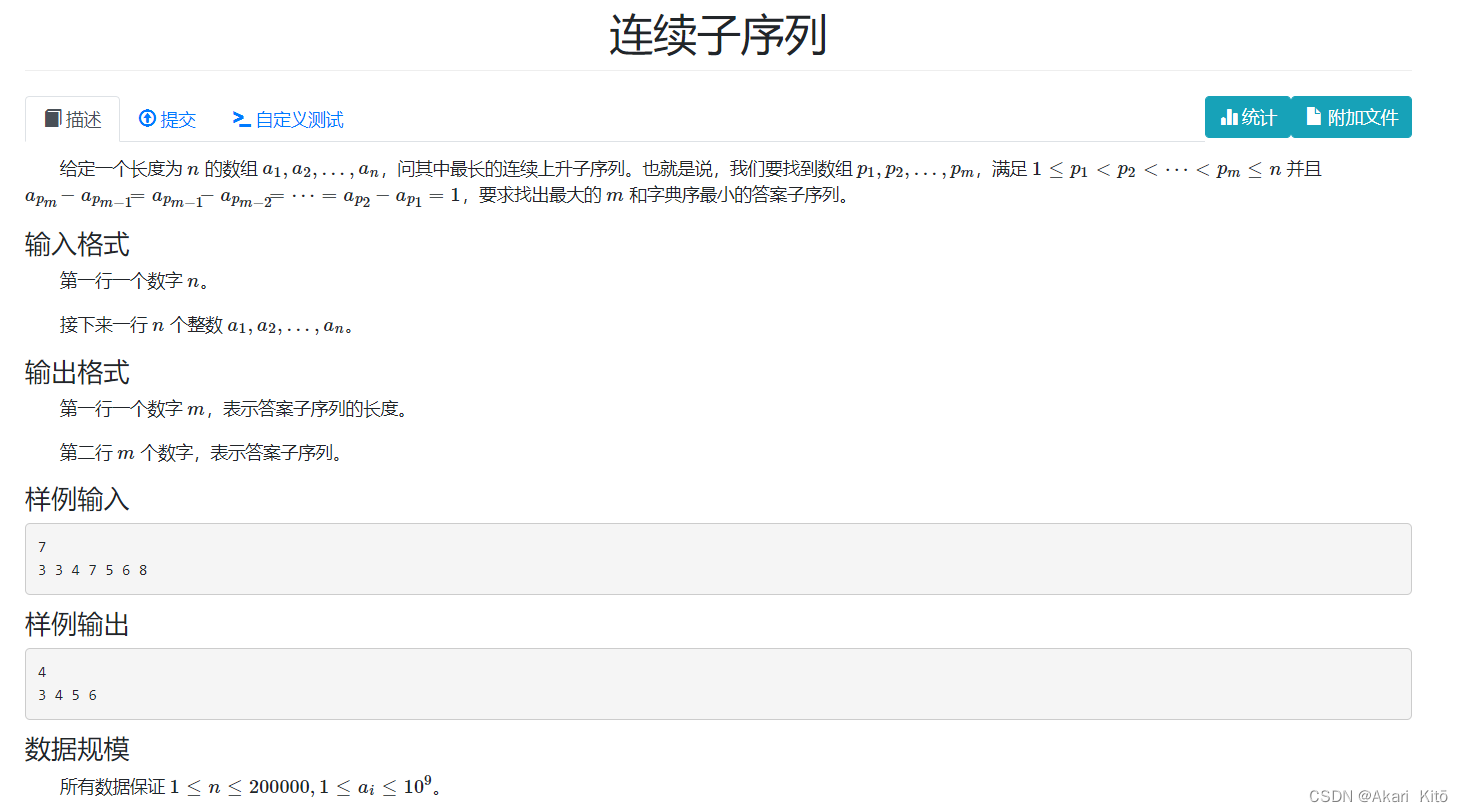
分析:
dp数组开成map,则状态转移式dp[i] = max(dp[i - 1] + 1, dp[i])
AC代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define int ll
#define endl '\n'
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
const int maxn = 2e5 + 5;
int n;
map<int, int> dp;
int ar[maxn];
signed main()
{
io;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> ar[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
if(!dp.count(ar[i] - 1)) dp[ar[i]] = 1;
else dp[ar[i]] = max(dp[ar[i]], dp[ar[i] - 1] + 1);
}
int mx = 0, id;
for(auto [x, y] : dp)
{
if(y > mx)
{
mx = y;
id = x;
}
}
cout << mx << '\n';
for(int i = id - mx + 1; i <= id; ++i) cout << i << ' ';
return 0;
}
|

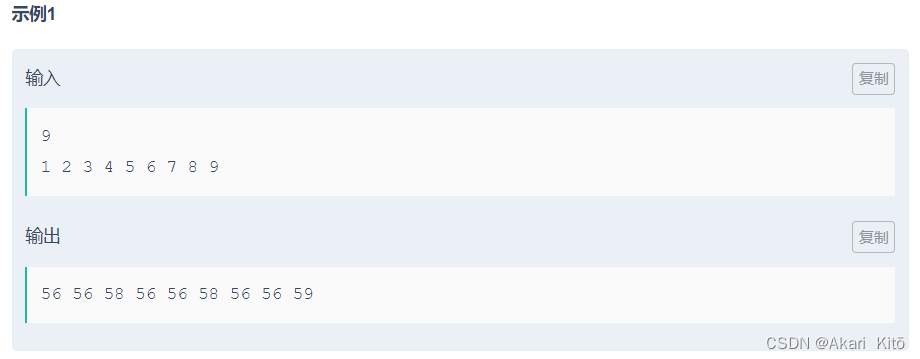
分析:
z = x + y
容易发现:z的数字根 = (x的数字根+y)的数字根
由此,定义dp[i][j](n * 10)表示前i个数字组出j的方案数
状态转移方程:dp[i][calc(j + ar[i])] += dp[i - 1][j]
AC代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define int ll
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define endl '\n'
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;
const int mod = 998244353;
int n;
int ar[maxn];
int dp[maxn][15];
int calc(int x)
{
int tmp;
while(x >= 10)
{
tmp = 0;
while(x)
{
tmp += x % 10;
x /= 10;
}
x = tmp;
}
return x;
}
signed main()
{
io;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> ar[i];
dp[0][0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
for(int j = 0; j <= 9; ++j) (dp[i][j] += dp[i - 1][j]) %= mod;
for(int j = 0; j <= 9; ++j) (dp[i][calc(j + ar[i])] += dp[i - 1][j]) %= mod;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= 9; ++i) cout << dp[n][i] << ' ';
return 0;
}
|

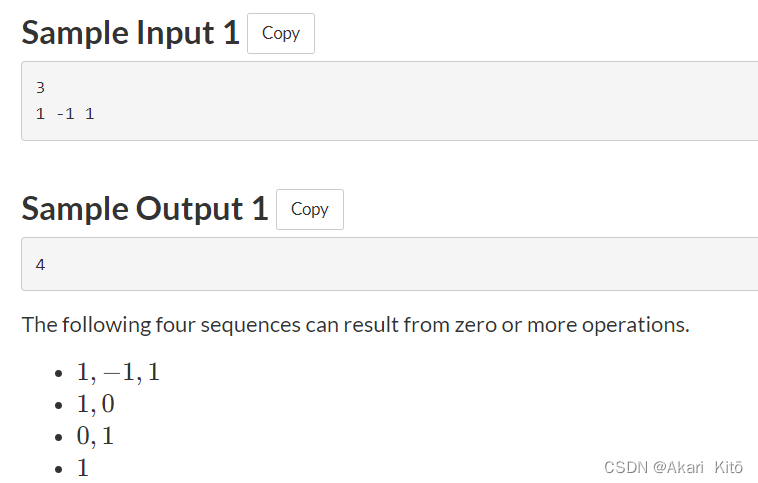
分析:
dp[i]表示操作前i个数字一共可以产生多少种不同的序列
新增数字ar[i]。
首先,将可以这个数字放在dp[i-1]种序列最后不做操作
其次,可以和dp[i-1]种序列的最后一个元素合并
但是,$dp[i] \neq dp[i - 1] \times 2$
因为会有重复的,我们将序列分为3段。
ar[1~j] ar[j+1~i-1] ar[i]
分成三段后,可以发现序列进一步合并的话,可以有两种情况,一是合并ar[1~i-1],形成序列ar[1~i-1] ar[i]。二是合并ar[j+1~i],形成序列ar[1~j] ar[j+1~i]。
可以发现,当且仅当sum[j+1~i-1]=0时两个序列是相同的,数量是dp[j]。
因此,只需要找到位置i左边的第一个j满足sum[i-1]-sum[j]=0即可,减去dp[j]。(前面满足条件的j的数量包括在左边第一个里面)。
AC代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define int ll
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define endl '\n'
const int maxn = 2e5 + 5;
const int mod = 998244353;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n;
int ar[maxn];
map<int,int> mp;
int sum[maxn];
int dp[maxn];
signed main()
{
io;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> ar[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + ar[i];
dp[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i)
{
dp[i] = (dp[i - 1] * 2ll) % mod;
if(mp.count(sum[i - 1])) dp[i] = ((dp[i] - dp[mp[sum[i - 1]]]) % mod + mod) % mod;
mp[sum[i - 1]] = i - 1;
}
cout << dp[n] << '\n';
return 0;
}
|

分析:
二分平均数和中位数。
对于平均数mid,构造数组br[i] = ar[i] - mid,之后定义dp[i]表示在满足条件下选完区间1~i且选取br[i]的最大值,转移方程dp[i] = max(dp[i - 1], dp[i - 2]) + br[i]。返回max(dp[n], dp[n - 1]) >= 0即可。
对于中位数mid同理,构造数组br[i] = ar[i] >= mid ? i : 0,相同的dp一遍即可。
AC代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define int ll
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define endl '\n'
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;
const int mod = 998244353;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-4;
int n;
int ar[maxn];
double br[maxn];
double dp1[maxn];
int dp2[maxn];
bool judge1(double x)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) br[i] = (double)ar[i] - x;
dp1[1] = br[1];
dp1[2] = max(0.0, br[1]) + br[2];
for(int i = 3; i <= n; ++i) dp1[i] = max(dp1[i - 1], dp1[i - 2]) + br[i];
if(dp1[n] >= 0 || dp1[n - 1] >= 0) return true;
else return false;
}
void work1()
{
double l = 0, r = 1e9;
while(r - l >= eps)
{
double mid = (l + r) / 2.0;
if(judge1(mid)) l = mid;
else r = mid;
}
cout << fixed << setprecision(4) << l << '\n';
}
bool judge2(int k)
{
dp2[1] = (ar[1] >= k ? 1 : -1);
dp2[2] = max(0ll, dp2[1]) + (ar[2] >= k ? 1 : -1);
for(int i = 3; i <= n; ++i) dp2[i] = max(dp2[i - 1], dp2[i - 2]) + (ar[i] >= k ? 1 : -1);
if(dp2[n] > 0 || dp2[n - 1] > 0) return true;
else return false;
}
void work2()
{
int l = 1, r = (ll)1e9;
while(l <= r)
{
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(judge2(mid)) l = mid + 1;
else r = mid - 1;
}
cout << l - 1 << '\n';
}
signed main()
{
io;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> ar[i];
work1();
work2();
return 0;
}
|
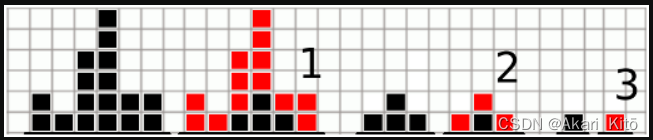
分析:
对于一列方格被完全删除掉,有三种情况,一是其左侧没有方格后,它会被删掉,我们认为它是被其左侧的方格删除,二是,其右侧没有方格后。三是其左右两侧的方格都足够多,它只能通过它自己一个一个的删除掉,这种情况需要操作h[i]次。
对于第一种情况,我们定义dp1[i]为第i列被其左侧删掉的情况需要操作多少次,转移方程dp1[i] = max(dp1[i - 1] + 1,h[i])。被其右侧删掉同理。
最后ans = max(ans, min(dp1[i], dp2[i]))
AC代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define int ll
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define endl '\n'
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;
const int mod = 998244353;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-4;
int n;
int ar[maxn];
int dp1[maxn];
int dp2[maxn];
signed main()
{
io;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> ar[i];
dp1[0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) dp1[i] = min(ar[i], dp1[i - 1] + 1);
dp2[n + 1] = 0;
for(int i = n; i > 0; --i) dp2[i] = min(ar[i], dp2[i + 1] + 1);
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) ans = max(ans, min(dp1[i], dp2[i]));
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
|

分析:
方法一:
首先,容易发现h[i]需要满足一些条件才会有解。
1.h[0] = 0,h[n] = n - 1
2.h[i] >= h[i - 1]
3.h[i] >= i - 1
之后,我们定义dp[i]表示对于区间1~i可以有多少种不同的数组a,对于状态转移方程,我们考虑两种情况。
1.h[i] = h[i - 1]
意思是说添加ar[i]后,h[i]不会发生变化,故g[i] < ar[i] < f[i],并且是前i-1个数中没有被选过的,这样的数字一共有ar[i - 1] - 1 - (i - 3)个,故此时dp[i] = dp[i - 1] * (ar[i - 1] - 1 - (i - 3))
2.h[i] != h[i - 1]
cx = h[i] - h[i] - 1,此时应当满足ar[i] = g[i - 1] - cx或者ar[i] = f[i - 1] + cx,所以大体上看dp[i] = dp[i - 1] * 2,但是不然,因为这样看的话ar[i]的取值可能取到小于等于0的数字,或者大于n的数字。我们考虑将这些不符合的减掉。
考虑ar[i]的放置时,前i-1个数字排序方式是不影响的,故我们考虑将选择了相同i-1个数字的数组看成同一种并将他们从小到大排序,之后在分类。
第1种: 1, i - 3个数字, h[i - 1] + 1
第2种: 2, i - 3个数字, h[i - 1] + 2
……
第n-h[i - 1]种: n - h[i - 1], i - 3个数字, n
容易发现每种ar[i]数组对应的原本数组数量是相同的(dp[i-1]种ar[i]数组中,通过排序变成第1种,第2种,…,第n-h[i-1]种数量是相同的)。
可以发现对于第1~cx种,ar[i]的取值只能是f[i - 1] + cx
对于第n-h[i-1]-cx+1~n-h[i-1]种,ar[i]的取值只能是g[i - 1] - cx
容易发现,这两者对应的数组种类也是不相交的,即满足n-h[i-1]-cx+1 > cx,故需要将这些减去。
转移方程dp[i] = dp[i - 1] * 2 - dp[i - 1] / (n - h[i - 1]) * 2 * cx
方法二:(idea from ygg)
整个过程相当于维护一个桶,对于h[i],需要一个大小为h[i]+1的桶
遍历1~n,过程中维护桶的大小siz和答案ans
如果h[i] + 1 > siz则需要将桶的上界或者下界扩大,即ans *= 2
否则,则需要向桶里添加数字,剩下的可添加的数字有siz - (i - 1)个,故ans *= siz - (i - 1)
AC代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define int ll
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define endl '\n'
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-4;
int t, n;
int ar[maxn];
int dp[maxn];
ll pow_mod(ll a, ll n)
{
ll ans = 1;
a %= mod;
while(n)
{
if(n & 1) ans = (ans * a) % mod;
a = (a * a) % mod;
n >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
void work()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> ar[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
if(ar[i] < ar[i - 1] || ar[i] < i - 1)
{
cout << 0 << '\n';
return ;
}
}
if(ar[1] != 0 || ar[n] != n - 1)
{
cout << 0 << '\n';
return ;
}
dp[1] = n;
int cx;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i)
{
cx = ar[i] - ar[i - 1];
if(cx) dp[i] = (((2ll * dp[i - 1]) % mod - ((2ll * dp[i - 1] * cx) % mod * pow_mod(n - ar[i - 1], mod - 2)) % mod) % mod + mod) % mod;
else dp[i] = (dp[i - 1] * (ar[i - 1] - 1 - i + 3)) % mod;
}
cout << dp[n] << '\n';
}
signed main()
{
io;
cin >> t;
while(t--) work();
return 0;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define int ll
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define endl '\n'
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-4;
int t, n;
int ar[maxn];
int dp[maxn];
void work()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> ar[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
if(ar[i] < ar[i - 1] || ar[i] < i - 1)
{
cout << 0 << '\n';
return ;
}
}
if(ar[1] != 0 || ar[n] != n - 1)
{
cout << 0 << '\n';
return ;
}
dp[1] = 1;
int cx;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i)
{
cx = ar[i] - ar[i - 1];
if(cx) dp[i] = dp[i - 1] * 2ll % mod;
else dp[i] = (dp[i - 1] * (ar[i] + 1 - i + 1)) % mod;
}
cout << dp[n] << '\n';
}
signed main()
{
io;
cin >> t;
while(t--) work();
return 0;
}
|

分析:
倍数遍历,nlogn,水题
AC代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define int ll
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define endl '\n'
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int maxn = 1e6 + 5;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps = 1e-4;
int t, n;
int ar[maxn];
int dp[maxn];
vector<int> vt[maxn];
void work()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%d", &ar[i]);
for(int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) dp[i] = 1;
int mx = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
for(int j = 2 * i; j <= n; j += i)
{
if(ar[i] < ar[j]) dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[i] + 1);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) mx = max(mx, dp[i]);
cout << mx << '\n';
}
signed main()
{
io;
cin >> t;
while(t--) work();
return 0;
}
|
分析:
观察发现,分割之后的每个序列如果内部不单调,那么一定不是最优的。
故可以分别考虑当前这个数在一个递增序列或者在一个递减序列的最大值。
AC代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define int ll
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define endl '\n'
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int maxn = 1e6 + 5;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n;
int ar[maxn];
int dp[3][maxn];
signed main()
{
io;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> ar[i];
for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i)
{
if(ar[i] > ar[i - 1])
{
dp[1][i] = max(dp[1][i - 1] + ar[i] - ar[i - 1], dp[0][i - 1]);
dp[0][i] = max(dp[1][i - 1], dp[0][i - 1]);
}
else
{
dp[1][i] = max(dp[1][i - 1], dp[0][i - 1]);
dp[0][i] = max(dp[0][i - 1] + ar[i - 1] - ar[i], dp[1][i - 1]);
}
}
cout << max(dp[1][n], dp[0][n]) << '\n';
return 0;
}
|
分析:
定义dp[i]为最后一个数字的第i位为1的序列的最长长度。
对于ar[i],枚举其每一位,假设其第j位是1,则dp[j]++,过程中维护mx=max(mx, dp[j])
之后将所有的dp[j]赋为mx
AC代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define int ll
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define endl '\n'
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int maxn = 1e6 + 5;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n;
int ar[maxn];
int dp[35];
void calc(int x)
{
int tmp = ar[x], id = 0, mx = 0;
while(tmp)
{
++id;
if(tmp&1)
{
++dp[id];
mx = max(mx, dp[id]);
}
tmp >>= 1;
}
tmp = ar[x];
id = 0;
while(tmp)
{
++id;
if(tmp&1) dp[id] = max(dp[id], mx);
tmp >>= 1;
}
}
signed main()
{
io;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> ar[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) calc(i);
int mx = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 32; ++i) mx = max(mx, dp[i]);
cout << mx << '\n';
return 0;
}
|
题意:
给定一个数字n(1<=n<=4e4),问n可以由多少种不同的回文数的相加表示。
对于5
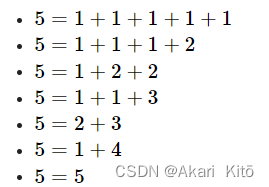
分析:
4e4内回文数一共不到500个,预处理处理,之后就是一个完全背包统计方案数的过程
AC代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define int ll
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define endl '\n'
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int maxn = 4e4 + 5;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int t, n;
int ar[maxn];
int dp[maxn];
vector<int> vt;
bool judge(int x)
{
int tmp = x, res = 0;
while(tmp)
{
res = res * 10 + tmp % 10;
tmp /= 10;
}
return x == res;
}
void init()
{
for(int i = 1; i <= maxn; ++i) if(judge(i)) vt.push_back(i);
dp[0] = 1;
for(int j = 0; j < vt.size(); ++j)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= 4e4; ++i)
{
if(i >= vt[j]) (dp[i] += dp[i - vt[j]]) %= mod;
}
}
}
void work()
{
cin >> n;
cout << dp[n] << '\n';
}
signed main()
{
io;
init();
cin >> t;
while(t--) work();
return 0;
}
|

分析:
对于小t的付款方式可以通过一个简单的dp1搞出来
对于最优的付款方式也是一个完全背包方案数的问题。
另外,具体要考虑到买多贵的东西,瞎猜的2*ar[n]正确了,据说实际到ar[n] + ar[n - 1]即可。
AC代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define int ll
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define endl '\n'
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int t, n;
int ar[maxn];
int dp1[maxn];
int dp2[maxn];
void work()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> ar[i];
int pos;
for(int i = 1; i <= ar[n] + ar[n - 1]; ++i)
{
dp2[i] = i;
pos = lower_bound(ar + 1, ar + n + 1, i) - ar;
if(ar[pos] == i) dp1[i] = 1;
else
{
--pos;
dp1[i] = i / ar[pos];
dp1[i] += dp1[i % ar[pos]];
}
}
dp2[0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
for(int j = 0; j <= ar[n] + ar[n - 1]; ++j)
{
dp2[j + ar[i]] = min(dp2[j + ar[i]], dp2[j] + 1);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= ar[n] + ar[n - 1]; ++i)
{
if(dp2[i] < dp1[i])
{
cout << "No\n";
return ;
}
}
cout << "Yes\n";
}
signed main()
{
io;
cin >> t;
while(t--) work();
return 0;
}
|

分析:
dp[i]表示集合中最大的数字是i的情况下,集合最大是多少,倍数遍历转移即可。
AC代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define int ll
#define io ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define endl '\n'
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int maxn = 2e5 + 5;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int t, n;
int ar[maxn];
int dp[maxn];
int num[maxn];
void work()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> ar[i];
sort(ar + 1, ar + n + 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= ar[n]; ++i) dp[i] = num[i] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) ++num[ar[i]];
for(int i = 1; i <= ar[n]; ++i) if(num[i]) dp[i] = num[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= ar[n]; ++i)
{
if(!num[i]) continue;
for(int j = 2 * i; j <= ar[n]; j += i)
{
if(!num[j]) continue;
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[i] + num[j]);
}
}
int mx = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= ar[n]; ++i) mx = max(dp[i], mx);
cout << n - mx << '\n';
}
signed main()
{
io;
cin >> t;
while(t--) work();
return 0;
}
|